1. Introduction to International Political Economy in IR
2. From Bretton Woods to WTO
3. Bretton Woods Institutions
3.1. Origin
3.2. Informal Regime/Pre-Bretton Woods Regime
3.3. Fixed Exchange Rate
3.4. Formal Regime/Bretton Woods Regime
4. 1.International Monetary Fund (IMF)
5. 2. World Bank
5.1. Differences between WB and IMF
6. Achievements of Bretton Woods Institutions
7. Limitations/Criticisms
8. Rationale in the Era of Globalisation

Hey champs! you’re in the right place. I know how overwhelming exams can feel—books piling up, last-minute panic, and everything seems messy. I’ve been there too, coming from the same college and background as you, so I completely understand how stressful this time can be.
That’s why I joined Examopedia—to help solve the common problems students face and provide content that’s clear, reliable, and easy to understand. Here, you’ll find notes, examples, scholars, and free flashcards which are updated & revised to make your prep smoother and less stressful.
You’re not alone in this journey, and your feedback helps us improve every day at Examopedia.
Forever grateful ♥
Janvi Singhi

Give Your Feedback!!
Topic – Evolution of International Economic Order: From Bretton Woods to WTO (Notes)
Subject – Political Science
(International Relations)
Table of Contents
Introduction to International Political Economy in IR
- Political Economy is not a new branch of social science; it evolved with the spread of capitalism in Europe.
- It advanced through academic discourses led by scholars like Adam Smith, David Ricardo, Karl Marx, Friedrich Engels, Max Weber and others.
- It examines how economic activities impact politics and statecraft, and how politics and economy interact with each other.
- International Political Economy (IPE) studies international relations through the lens of global economic activities and their analyses.
- The onset of globalization from the mid-1980s revived scholarly interest in IPE.
- Modern IR now integrates economic analyses along with political and security perspectives.
- The significance of trade and commerce in international relations remains strong.
- Economic institutions like the WTO, IMF, and FTAs increasingly influence global politics.
- The rising importance of Multinational Corporations (MNCs) shapes contemporary world politics.
- Due to these developments, IPE has become one of the most significant areas in the study of international relations.
- IPE covers a vast scope, including:
- International trade regime
- International monetary regime
- International investment regime, focusing on institutions, organizations, and economic activities
- FTAs among states
- Economic development and global disparities
- Globalization
- The North–South divide
- The future of capitalism and socialism
- These issues have generated academic debates and produced multiple theories in IPE.
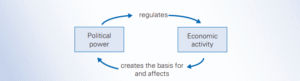
- The international economic system promotes free trade, free investment, free markets, and strict market discipline, but it is rooted in the economic models of developed countries.
- The world economy today is vastly different from what it was 60+ years ago when the system was first established.
- The global economic landscape has undergone major changes since the end of the Cold War.
- The global financial crisis introduced a “new normal” in the world economy.
- New challenges have emerged that the current global governance system struggles to address effectively.
- The post–World War II economic architecture was largely shaped by the United States.
- Institutions like the IMF, World Bank, and GATT were created to establish a liberal international economic system.
- The Marshall Plan enabled the USA to expand its influence and support the economic rebuilding of its allies.
- In the 1970s, U.S. hegemony declined, giving rise to demands from developing countries for a New International Economic Order (NIEO).
- The Bretton Woods system collapsed in 1973, compelling the USA to coordinate macroeconomic policies with other developed nations.
- The 1997–98 Asian financial crisis cast doubt on the IMF’s governance and the Washington Consensus.
- The crisis led to greater regional cooperation in Asia.
- The 2007 U.S. subprime crisis and the European sovereign debt crisis exposed vulnerabilities in developed economies.
- Regional and cross-regional platforms have become essential in addressing global economic challenges.
- These platforms aim to detect, prevent, and resolve issues worsened by globalization.
- Regionalization has expanded, with new institutions and agreements to manage globalization-related pressures.
- Key examples include the strengthening of BRICS, the multilateralization of the Chiang Mai Initiative, and the rise of mega-regional FTAs such as RCEP, TPP, and TTIP.
From Bretton Woods to WTO
- As the Second World War neared its end, Allied leaders began planning the post-war global political and economic order.
- In July 1944, 730 delegates from 44 Allied nations met at Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, during the UN Monetary and Fiscal Conference.
- The conference concluded with the signing of the Bretton Woods Agreement to regulate the post-war international economic system.
- The agreement created the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) (now part of the World Bank Group).
- These institutions became operational in 1945 after ratification by participating countries.
- A key feature was that countries must maintain fixed exchange rates, ensuring currency stability.
- The primary aim was to prevent currency disorders and stabilize exchange rates through a regulated economic system.
- The IMF was tasked with addressing temporary balance of payments imbalances.
- Bretton Woods leaders favored a regulated market system with strict controls on currency values.
- Although implementation methods were debated, all agreed on tight controls, influenced by the Great Depression and wartime economic setbacks.
- The agreement was grounded in Keynesian economics, which supported a controlled market economy with state intervention.
- Keynesian thinkers supported free trade, reduced tariffs, and a liberal market economy, but with the state remaining visible in economic activities.
- The international system required high cooperation among states, monitored by institutions like the IMF and IBRD.
- Economic crises between WWI and WWII were blamed on poor cooperation and the absence of regulatory institutions.
- Bretton Woods sought to correct these flaws by creating cooperative and supervisory bodies, laying the foundation for the modern international economic system.
- This system still depends on state cooperation, though private economic actors now play a major role.
- In line with Bretton Woods, the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) was created in 1947 to shape the international trade regime.
- While IMF and IBRD governed monetary and investment regimes, GATT governed trade.
- Plans for an International Trade Organization (ITO) failed in 1946, so GATT emerged as a treaty, not an organization.
- GATT became operational on 1 January 1948, signed by 23 countries.
- Its core objective was to reduce global trade barriers, achieved through lowering tariffs, restricting quotas, and regulating subsidies.
- From its first round in Annecy (1949) to the Uruguay Round (1986–1993), GATT achieved 45% reduction in global tariffs.
- By 1993, tariff concessions valued at US$1,200 billion had been secured.
- Membership expanded from 23 countries (1948) to 123 countries in the Uruguay Round.
- GATT negotiations covered non-tariff barriers, services, IP rights, dispute settlement, agriculture, textiles, labour, competition, environment, and investment rules.
- The Uruguay Round decided to establish the World Trade Organization (WTO) to replace GATT as the central authority for monitoring the international trade regime.
- The WTO became operational in 1995 after the Marrakesh Agreement.
- With 153 member-states, it represents 90% of global trade.
- Its membership, functions, structure, and impact on world economy and politics are discussed subsequently.
International Relations Membership Required
You must be a International Relations member to access this content.
